R
RabbitMQ™ Software
A lightweight open-source message broker software that implements the Advanced Message Queuing Protocol (AMQP) and other protocols.
RAC
See real application clustering (RAC).
radio access network (RAN)
The part of a mobile telecommunication system that connects a device such as a mobile phone, computer, or any remotely controlled machine to a core network via a radio connection.
In Itron’s Fixed Network, the communication network connecting cell control units (CCUs) to endpoints is a RAN.
radio carrier frequency
The radio frequency used by a data collection device to transmit a wake-up tone to an Encoder/Receiver/Transmitter (ERT) module. ERT modules that use wake-up tones wait until they receive a wake-up tone before transmitting their meter reading and tamper data in a standard consumption message (SCM). To wake up an ERT module, a data collection device emits a utility-specific wake-up tone using a radio frequency of 952 MHz or 956 MHz. Each ERT module can receive a range of carrier frequencies but only responds to the wake-up tone it is programmed to recognize. A utility must receive a license from the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) or Industry Canada (IC) for a specific carrier radio frequency to legally operate a data collection device at that frequency.
radio frequency (RF)
The rate of oscillation of transmitting waves of a given radio message or broadcast. RF is the electromagnetic field generated by AC current that is suitable for wireless communications.
radio-frequency communications block
An Encoder/Receiver/Transmitter (ERT) module component that receives a wake-up signal from and transmits data to a data collection device.
Radio-Frequency Configuration Tool (RFCT)
The configuration tool used by Itron international RF devices to configure them. It is used to read, configure, and check radio devices like: AnyQuest Cyble, EverBlu Cyble, Cyble 5, RF Option Board, and Intelis Water Meter.
radio-frequency local area network (RFLAN)
An Itron-proprietary local area network (LAN) consisting of an OpenWay cell relay and the CENTRON meters that communicate with it through radio frequency connections. Each cell relay can support up to 2000 meters. Connectivity between a meter and a cell relay can be direct, through another smart meter, or through multiple layers of smart meters. The RFLAN network is dynamic and self-healing. If the connection between a meter and a cell relay is broken or blocked, the meter locates another connection path through the network mesh to the cell relay.
RADIUS
See Remote Authentication Dial-in User Service (RADIUS).
RAID
See redundant array of independent disks (RAID).
RAM
See random access memory (RAM).
RAN
See radio access network (RAN).
random access memory (RAM)
A type of computer memory, usually in the form of semi-conductor chips, that the central processing unit (CPU) and other devices write information to and read information from. Information in RAM can be accessed randomly, in any order, without regard to the order in which it is stored. RAM normally holds data only while the computer is turned on and loses it when the computer is turned off.
Random phase multiple access (RPMA)
A combination of technologies owned by Ingenu which are designed for wireless machine-to-machine communication.
Range Extender
An additional node in a network that builds density or extends the perimeter of the existing network.
Rapid Demand Response (DR) Telemetry
A sensor that supports demand response at all times of the year with up‐to‐the‐minute data collected on DR event performance for all DR customers and facilitates integration of distributed energy resources.
Raspberry Pi®
A computing solution that fits a wide range of applications. From micro-controllers to ARM-based computers, it provides robust computing power and low power draw.
rate base
The value of assets and property on which a utility is permitted to earn a specific rate of return. Rate base is usually established for a utility by a regulatory body such as the Public Utilities Commission (PUC).
rate limitation
Refers to a limitation of the number of critical command that can be issued within a configured length of time to protect the security of the power grid. Disconnect and connect are examples of critical commands that can only be issued by individuals authorized to do so.
rate plan
See regulated price plan (RPP).
rate structure
The various rates charged by a utility for its services.
rate threshold
A sliding window of time during which permits can be issued and, correspondingly, users can issue a valid critical command, such as a disconnection of service. After this time limit has expired, no permit is issued.
raw materials inventory (RMI)
The total cost of all product components in stock that have not been and are not yet being used to manufacture the product.
RBAC
See role based access control (RBAC).
RDBMS
See relational database management system (RDBMS).
RDS
-
Remote Disconnect Switch
-
Remote Disconnect Service
reachable
The ability to send and receive data to and from a meter. A reachable meter is usually readable. However, a meter may be reachable with small packet sizes, but may not be readable with the larger packet sizes necessary for a successful read.
reactive energy
The electrical energy produced, flowing, or supplied by an electric circuit during a time interval, measured in units of kilovolt-ampere reactive hours (kVARh) or standard multiples thereof. It is the integral of reactive power with respect to time.
reactive power
The dissipated power resulting from inductive and capacitive loads measured in and symbolized by the letter Q.
In electrical grid systems, the power that flows back from a destination toward the grid in an alternating current scenario. In a direct current system, the voltage and load is static, and the direction of energy is "one way," but in alternating current, there are different phases.
For sinusoidal quantities in a two-wire circuit, reactive power is the product of the voltage, the current, and the sine of the phase angle between them with the current taken as reverence. In a polyphase circuit, it is the sum of the reactive powers of the individual phases.
The following figure is the Power Triangle. The Power Triangle relates true (P), reactive (Q), and apparent power (S) in trigonometric form.
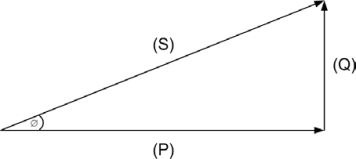
Reactive power is also known as phantom power or wattless power. See also kVAR lead.
reader
A cell control unit (CCU or collector) or repeater in an Itron Fixed Network system.
read (meter read)
The collection of usage data from a meter. Collections of meter reads are referred to as read data.
read schedules
Defined time periods within which meter readings are collected.
read success rate (RSR)
Percentage of meter reads saved to the relational database management system (RDBMS) during a 24-hour period. For example, the default interval schedule reads meters every two hours or 12 times per day. If a meter is read 11 times, the RSR is 92%.
The RSR is a useful metric for determining the reachability of a meter during various times of day. This data determines at what times of day meter reachability declines so administrators can plan schedules accordingly. Unlike BSR, which is a metric for successfully completed, intact meter reads that correspond to a business rule (completed reads from midnight to midnight), RSR is a metric for meter reads per schedule. See also billing success rate (BSR) and message success rate (MSR).
ready to secure
A security level employed by ChoiceConnect endpoints that support enhanced security, such as Itron’s 100 series endpoints. In ready-to-secure mode enhanced security is not enabled and the endpoint employs only the kind of basic security features supported by Itron’s earlier endpoint types.
real application clustering (RAC)
A shared disk clustering technology that is used to run multiple databases instances against shared data files. over multiple hardware systems. Using RAC, multiple hardware systems in the cluster appear as a single database to the application. Most often refers to Oracle RAC, which is Oracle's premier disk clustering technology.
real time pricing (RTP)
Enables frequent price adjustments based on real-time market conditions. Prices may change hourly, with one-hour or one-day notice, and are based on actual wholesale prices or on statistical models that forecast wholesale prices. Customers are notified in advance of the price change, allowing them time to curtail demand. See also critical peak pricing (CPP) and time-of-use (TOU) rate.
real-time clock (RTC)
A computer clock, usually an integrated circuit, that keeps track of the current time.
real-time data
Real-time or near-real-time data collection is the ability to collect data automatically on demand, and have the data analyzed immediately to effect monitoring and control decisions. This can be data directly collected from the meter (real-time) or logically derived from data in the database (near-real-time). Real-time or near-real- time data collection is a key component of Smart Grid Technology.
real-time pricing
Electricity rates that reflect the actual moment-by-moment cost of providing electricity.
reboot counter
This counter, which resides within the last gasp (LG) trap having preceded it, due to the LG trap having been lost.
received signal strength indicator (RSSI)
A circuit that measures and indicates the strength of an incoming (received) signal in a receiver. A common example is the signal strength indicator on a cell phone.
recloser
A switch or circuit breaker that re-establishes an electrical circuit manually, remotely, or automatically after an interruption of service.
reclosure
In an electric utility distribution system, functionality executed by a recloser, which automatically opens and closes a circuit in response to a temporary interruption, such as a lightning strike, so that the fuse does not have to be replaced.
Recommended Standard 232 (RS-232)
A series of telecommunications standards for the electrical characteristics of data terminal equipment connectors, such as computers; and remote devices such as modems, printers, and display screens.
Characteristics defined in the standards include serial binary single-ended data and control signal timing, connector pinout meaning and signal direction, and the number of pinouts and their physical size and arrangement on the connector.
reconfiguration
In the context of a system, device, or application: rearranging elements and settings.
In the context of OpenWay, specified variables being written to the meter. Items not specified are not set to empty or written from program data.
recorder
A device that records a metered quantity, such as an ERT (encoder-receiver-transmitter radio-based module) or an interval data recorder. A meter can have multiple internal or external recording devices.
Recorders are devices that log load profile data. Other terms for recorders are loggers, data loggers, data recorders, or recording devices. Recorders can often be called, or will initiate a call, remotely through a modem or other communications technology.
recorder-under-glass (RUG)
A type of electric meter in which the meter and interval data recorder (IDR) are combined in one device. The recorder identifier (ID), manufacturer, and model are the same as the meter's.
Recorder-under-glass (RUG) is also called a combined meter.
recovery key
An asymmetric, elliptic curve cryptography (ECC) key that consists of a public and a private component and is unique to each OpenWay CENTRON Meter. A recovery key is placed in each meter during manufacturing and used to prove the meter’s authenticity to the OpenWay Collection Engine (CE) when the meter attempts to register. Recovery keys are also used to encrypt messages sent to meters containing other types of keys.
recovery point objective (RPO)
An amount of time, as determined by the utility, that defines the point in time to which data must be recovered after an outage. The number of minutes that an energy provider determines is an acceptable loss of data. For example, if the utility determines that their RPO is 15 minutes, then after the system recovers from a failure, data must be restored to within 15 minutes of the beginning of the failure. The data must be restored to within 15 minutes of the beginning of the failure, even if it took longer than 15 minutes for the system to be restored. The RPO is not how long the system can be down, but the acceptable amount of data that can be forfeited during the down-time.
redundancy
The number of readers that reported for a repeater or endpoint on a given day. For example, if two cell control units (CCUs) and one repeater reported for an endpoint during the reporting day, the endpoint has a redundancy of three.
redundant array of independent disks (RAID)
A method of storing the same data in different places (thus, redundantly) on multiple hard disks.
reference electrode
An electrical conductor with a stable and well-known electrode potential. The high stability of the electrode potential results from a redox system with constant concentrations of each component of the redox reaction. A reference electrode is used as a half cell to build an electrochemical cell.
reflection
When a propagating wave impinges on an object which is large compared to its wavelength and bounces off.
regional transmission organization (RTO)
An independent organization that coordinates, controls, and monitors the operation of the electrical power system and supply in a particular geographic area; similar to an independent system operator.
register
A readable device within a meter. For example, the demand or usage register read to calculate billing.
register
The component of an electricity, gas, or water meter that records consumption. There are five register types in the OpenWay meter: Energy, Demand, Instantaneous, Self-Read, and Information.
registered
The state of a device or user authorized to access program resources. The device or user must provide credentials to authenticate identity.
register multiplier
A programmable value used by a meter to calculate the energy and demand readings it displays or uses as a custom multiplier for special billing system requirements. For the OpenWay CENTRON Meter, the register multiplier is set to 1.00 and cannot be edited in the Collection Engine.
register read
Refers to a meter’s register information being transmitted across the network for use in the utility back office. For example, for billing purposes.
register settings
Configurable parameters that define interval lengths, power outage recognition time, cold load pickup time, and other settings. An endpoint must register with the OpenWay Collection Engine before communications can begin. See also register operation parameters.
Registrar
A software component and dynamic domain name system (DNS) server with a primary purpose to collect network registration and update notices from NIC-enabled devices sent using the DDNS protocol and to handle look-up requests per the DNS RFC (RFC1035). Its secondary purpose is to collect statistics from activity of the devices and to provide those statistics through a Representational State Transfer (REST) web service interface. See also Representational State Transfer (REST).
regulated price plan (RPP)
An electricity pricing plan that provides stable and predictable electricity pricing, encourages conservation, and ensures that the price consumers pay for electricity best reflects the price paid to generators.
relational database management system (RDBMS)
A program that allows you to create, update, and administer a relational database. Most relational database management systems use the SQL language to access the database and data is organized into tables. Oracle is an example of an RDBMS.
Relay
A device on a network used to extend the reach of a network. Relays are typically placed high for best line-of-sight to meters, and can be plugged into photocell sockets on light poles. Normally, several meters are associated with each Relay and several Relays are associated with an Access Point (AP).
Meters can also act as a Relay. Referred to as repeaters in utility and other networks. See also reachable.
Remote Authentication Dial-in User Service (RADIUS)
A distributed client/server protocol and software providing centralized authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) management to secure networks against unauthorized access.
remote CHAP password
See Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP).
remote device
A device controlled by a master device. A remote device is typically deployed as an edge network device, while a master device is typically deployed as a core device. Previously known as a slave device.
remote disconnect
Disconnecting a device from the back office (instead of at the physical site location of the device).
remote provisioning
See remote service management (RSM).
remote service management (RSM)
Refers to any job that acts on the remote disconnect, remote service, load control, or auxiliary switches.
remote terminal unit (RTU)
A device that interfaces objects in the physical world to a distributed control system or Supervisory Control And Data Acquisition (SCADA) by transmitting telemetry data to the system and/or altering the state of connected objects based on control messages received from the system. See also intelligent electronic device (IED).
Repeater 100
A component of Itron ChoiceConnect systems that continuously forwards meter data from nearby endpoints to a ChoiceConnect Cell Control Unit 100 (CCU 100). The CCU, in turn, sends the information to Fixed Network or mobile collection application software. Repeaters communicate with gas and electric endpoints and the CCU in the 900 MHz radio band.
repersonalizing
Downloading a new certificate and credits to a Field Service Unit (FSU).
replay attack
A form of a network attack in which a valid data transmission is maliciously repeated or delayed. For example, repeatedly sending a fraudulent message to another meter to attempt to retrieve information from that meter.
reporting day
The 24-hour period from midnight to midnight, UTC.
report list
The list of devices for which a cell control unit (CCU) or repeater is configured to relay reads. If a CCU or repeater has a report list, it filters out readings for all devices not on the list.
Representational State Transfer (REST)
A style of software architecture for distributed hypermedia systems such as the web.
re-queue
When Advanced Metering Manager (AMM) application, or requeues it, and polls the next meter in the queue.
When the schedule reaches the end of the queue, it starts again with re-queued meters. See also retries.
reserve margin
The amount of unused available capability of an electric power system at peak demand for a utility system, expressed as a percentage of total capability.
residential inclining block (RIB)
A rate schedule for residential utility customers under which a higher rate is charged for consumption over a specified amount per billing period. It is intended to encourage conservation.
residential meter
A watt-hour meter used to measure energy flow in a single phase of multiple currents fluctuating in unison. Single-phase meters are typically used for residential and light commercial service locations. Also called single-phase meter.
REST
See Representational State Transfer (REST).
restore time objective (RTO)
During a period when data is being recovered, measures the amount of time that an organization will not have access to a category of data.
result set
Data in tabular form displayed on the screen. For example, if a user performs a search for all meters of a particular model, all the meters that display constitute the result set.
retries
When a schedule is unable to read a meter on the first try, all subsequent attempts to read the meter are retries.
Retroset Pay
A component of the ChoiceConnect pay solution, Retroset Pay offers smart payment capabilities for commercial & industrial (C&I) applications. Built upon a robust shut-off valve, Restroset Pay allows utilities to ensure revenue collection.
return materials authorization (RMA)
Part of the process that allows a customer to return a material, product, or goods to the manufacturer for a refund, replacement, or repair. The RMA provides the customer and the manufacturer with a trackable authorization number for the return. Also called return merchandise authorization and return merchandise agreement.
return-to-utility (RTU) work order
A work order with a problem or issue that prevents a field service representative (FSR) from completing it and which therefore requires attention by personnel at the utility’s main office.
Revenue Assurance
An Itron solution that offers analytics, tools, and workflow support to facilitate detecting, investigating, and resolving lost revenue.
reverse flow
Occurs when a meter runs backwards. Either the meter was installed backward, which would result in a consistently decrementing read, or flow is actually being generated into the meter. Reverse flow conditions could indicate a stuck or defective meter or register. Electric and water endpoints may be capable of reporting reverse flow.
reverse power flow
When power flows in the opposite direction from its usual flow.
RF
See radio frequency (RF).
RF2Net
An Itron technology research project, completed in 2004, to develop a two-way communications network that is self-forming, self-healing, and scalable.
RFCT
See Radio-Frequency Configuration Tool (RFCT).
RFLAN
See radio-frequency local area network (RFLAN).
RFLAN processor
An OpenWay CENTRON Meter’s processor for managing its interface to the radio-frequency local area network (RFLAN).
RF Master 5
An all-purpose, walk-by/drive-by reader and programmer for use with Itron’s meter equipped with radio interface (wMbus compatible).
RF Mesh
A dynamic and self-healing Cisco proprietary mesh network consisting of a cell relay and the smart meters that communicate with it through radio frequency connections.
RIB
See residential inclining block (RIB).
rich client
A computer or program that requests data, files, or services or accesses shared network resources from a server computer or program. Of the client classes, rich client, hybrid client, and thin client, a rich client relies upon the server for little to no data processing. Most rich client functions can be performed without a connection to the server.
rightsizing
Analysis of consumption data recorded by a meter to determine if the meter is of the correct capacity to measure that level of consumption.
Rivest-Shamir-Adleman (RSA)
An algorithm for public-key cryptography that can be used for both encryption and signing.
RMA
See return materials authorization (RMA).
RMI
See raw materials inventory (RMI).
RMS
Robot Toolkit
A Java-based framework that offers scripts that remediate a variety of application-layer network problems by examining and acting on the Communication Module (NIC) of an endpoint. Robot allows users to run batches of network library commands against a list of meters.
role
A pre-defined set of user privileges that define functional security within a software application, controlling what actions a user can take. For example, you might assign some users to view-only roles for reports, while other users can also create and schedule reports.
role based access control (RBAC)
An access control mechanism where access permissions apply to groups of individuals that have been assigned the same role. Typical roles are administrator, user, and operator.
rolling demand interval
A method of measuring power or other quantities by taking measurements within fixed intervals of the demand period.
rolling interval demand
A calculation of maximum demand derived from the moving average of the smaller consecutive sub-intervals.
root key
The top-level public key / private key pair of the Certificate Authority (CA). If the private part of the root key is ever discovered, all the certificates issued under that key pair are compromised.
root mean square (RMS)
A statistical measure of the magnitude of an AC signal or peak modulation.
rotations per minute (RPM)
For gas meters, the number of rotations per minute of the wriggler, or per signal from the pulser.
round-robin DNS
A load-balancing method in which multiple servers take turns responding to network requests. A round-robin domain name server (DNS) algorithm continuously directs network traffic to the server next in line, regardless of the number of connections.
route
The route from an endpoint to an egress device, usually an Access Point (AP) or a Bridge Master. Routes are discovered dynamically. However, when performing an On Demand ping in Advanced Metering Manager (AMM) application, users can specify a one-time route that is discarded after use.
route cost
See path cost.
route ID
A meter reading route identification number including area number, route number, and cycle number.
Router Rules
An installable set of routing rules for each Itron application that uses them. Routing rules determine whether a trap is published to a JMS queue.
rpm
See rotations per minute (RPM).
RPMA
See Random phase multiple access (RPMA).
RPO
See recovery point objective (RPO).
RPP
See regulated price plan (RPP).
RS-232
See Recommended Standard 232 (RS-232).
RSA
See Rivest-Shamir-Adleman (RSA).
RSM
See remote service management (RSM).
RSR
RSSI
See received signal strength indicator (RSSI).
RTC
RTO
RTP
See real-time pricing.
RTU
See remote terminal unit (RTU).
See return-to-utility (RTU) work order.
RTU work order
See return-to-utility (RTU) work order.
rubber duck antenna
An antenna designed for indoor use and testing purposes only in conjunction with an Itron Bridge. It is suited for 900MHz ISM band applications, as well as 900MHz cellular applications. The rubber duck antenna has a tilt-and-swivel SMA-male connector, allowing it to be aligned at any angle.
RUG
See recorder-under-glass (RUG).
rule
A user-defined limit that allows or denies permits for load shedding events and critical command.
run
A schedule run consists of the initial attempt and all retries of all meters associated with the schedule, plus the initial attempt and all retries of requeued meters.
rural electric cooperative
A nonprofit, customer-owned electric utility that distributes power in a rural area.