Line sharing daisy chaining
Meter pooling
Meter Pooling is the method used by Service Mode to support daisy chain communications (where more than one meter is on a specific phone number/IP address). This is an optional method for handling daisy chain communications with MV-90 xi. However, it is mandatory for Service Mode.
Meter Pooling is enabled based on the existence of a Pervasive database table on the Service Mode Server (POOLWRKR.V90) located in the xiserv\master directory. If this file is not present you need to create it using Database Utilities and the Create function. Without this table, daisy chain communications cannot be performed.
Meter Pooling utilizes the PoolWorker database table which acts like a daisy-chain task list. The device designated as master will have a task in the task list (viewed from the Monitor UI). The master and all the slaves that were scheduled will also appear in the pool worker table. The contents of the pool worker table can be done using the Service Mode client UI by running Poolwrkr.exe from the \mv90xi directory (or from the Database menu).
MV90 recording device setup
To set up daisy chaining within MV90 Recording Device, use the Daisy Chain field to define the linked meters that are members of the daisy chain line sharing or pool. Select line sharing and one meter/recording device must be designated as a Master. Usually, this is an arbitrary assignment since on most daisy chain configurations, each meter is individually addressable. The Master ID (Recording Device ID—not External Recording Device ID) of the Master should be placed in the Daisy Master Record ID field. All slave devices and the designated Master Recording Device ID is placed in the Daisy Master Record ID field. It is not required to place any ID in the Daisy Slave Record ID field unless it is required to read specific slave meters in a specific order. This is due to the fact that meter pooling is used, rather than the legacy method of daisy chaining. There is no need to link all members of the chain, making maintenance much easier.
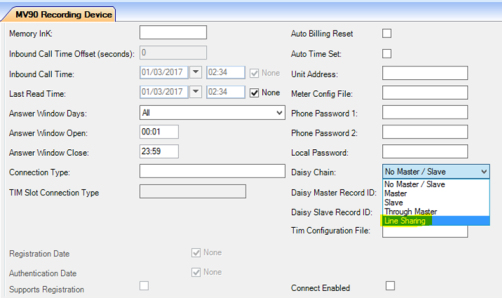
Line sharing daisy chaining task scheduling
If any chain member on a daisy chain is selected to be read when scheduling a manual remote interrogation task, an option appears to specify whether the entire chain should be read.
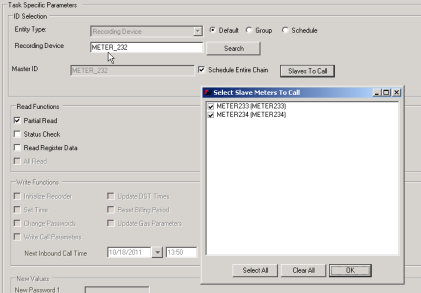
It is possible to read one or more of the meters on a daisy chain when scheduling the remote interrogation tasks (selecting Slaves to Call). When the task is scheduled in IEE, it appears as a single remote interrogation task in the Task Monitor.

In Service Mode the Master Meter appears in the task list. Running Poolwrkr.exe will show the individual slaves that were scheduled.
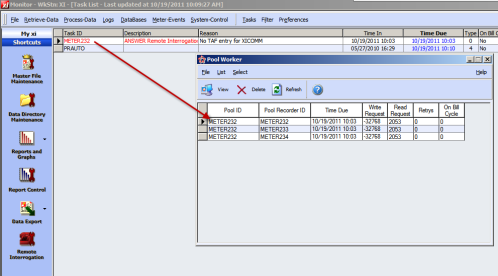
In IEE, the remote interrogation task is associated with the interrogation of all the meters scheduled to be read that are part of the chain. Viewing the Child Tasks views the individual ReadingXMLImportEnhanced tasks for each of the slave meters if they were read successfully.
If one of the meters on the daisy chain did not read successfully, a failed task is generated. If the other meters read successfully, the initial manual remote interrogation task has a success status. Viewing the Child Tasks of the primary manual remote interrogation task displays the associated failed task, as well as the successful interval import tasks for the other daisy chain components that were read successfully.
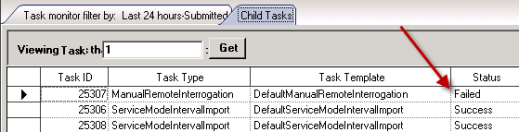
This can make troubleshooting daisy chain issues complex to troubleshoot using the Task Monitor, since the primary task shows success. The Remote Interrogation Queue is designed to focus only on the communication exceptions, showing no reference to the successful tasks.