Configuring service order import task adapter
The Service Order Import Task Adapter allows you to import service order information from an external system into IEE.
Use the following procedure to configure a task template:
-
Go to System Operations > Task Management > Task Templates.
-
Use the dropdown menu to select the Task Type and Task Template. (Click Add to create a new task template. For more information, see Adding task templates.)
-
Configure the Task Specific Parameters. These parameters are defined after this procedure.
-
Configure the Common Task Template Parameters. For more information, see Task template parameters.
-
Click Save.
Task specific parameters:
-
Processing Chunk Size. Defines the number of configuration entities processed by sub-tasks. IEE groups the data that was processed by the task into separate batches of the size you designate here. IEE considers the task completed when all child tasks are finished, and each has reported back to the parent tasks.
Chunk size is a parameter common to several task templates. The higher the chunk size value, the greater the portion of the total available work each IEE task runner performs. A smaller value means dividing the work between more concurrent task runners.
Chunk sizes that are too large overburden a few task runners, while other task runners sit idle. In extreme cases, overly large chunk sizes could result in system failure due to lack of available, allocated memory. Chunk sizes that are too small spawn many task runners that perform more initialization and shutdown than actual work. Both large and small extremes will cause delays in export processing.
When fine tuning chunk sizes, consider database resources, hardware requirements, daily processing levels, and processing windows. Adjust values over time, as hardware and networking conditions change.
-
Import Directory. Defines the folder that IEE monitors for incoming files. IEE automatically schedules files that arrive in this directory for import. You define the paths to default import directories in the IEE System Administration workbench. When configuring the import directory parameter in an import task template, enter the file path to the directory that IEE monitors for import files specific to this task. This parameter supports standard IEE macros. Reference as ($ImportDirectory) when configuring a task.
-
File Mask. Defines a file extension or a partial file name that IEE uses to monitor import directories and create export files. Enter a file mask such as .xml when configuring an import or export task template. When a file arrives in the import directory, IEE automatically schedules the file for import if it matches the mask. IEE ignores files that do not match the file mask. When creating an export file, IEE appends this mask to the file name.
-
Owner of Import Tasks. Defines the user ID associated with a task. By default, this box populates with the user currently logged into IEE.
-
Create Resubmit File. Determines whether IEE creates a file containing any import data that failed, along with any error messages reported. IEE places the resulting file into a resubmit directory under the import data folder. The file can be re-imported without change if it failed due to incorrect system data. Select True to enable this setting. Select False if you do not want the task to create a resubmit file.
-
Completing Task Template and Task Scheduler Parameters. Some or all of the following parameters display in the Task Template and Task Scheduler windows. The available parameters depend upon the type of task selected.
Common Task Template Parameters:
-
Requested Server. Defines the server to use to process the task. Select First Available if it does not matter which server processes the task.
-
Requested Start Date. Defines the date and time (hh:mm) to begin processing the task. Click the dropdown arrow to open a calendar.
-
Priority. Defines the task priority (0-99). IEE processes tasks in order of priority. The lower the number, the higher the task priority. Servers process tasks with higher priority (such as 15) before tasks with lower priority (such as 75). Administrators can configure task runners (IEE 6.x) and task services (IEE 7.x and later) to process only tasks with a particular minimum priority.
-
Description. Describes the task template. Enter a unique description if you have added a new task template for the selected task type. Once saved, this description displays in the Task Template dropdown menu. To run or modify this task template in the future, select the Task Type, and then select this description from the dropdown menu. You can create multiple task templates for each task type. It is possible to save multiple task templates with the same description, but Itron recommends using unique descriptions to make it easier to select the correct task template.
-
Task Significance. Defines the reason a particular set of data was exported. Task significance helps distinguish exports run on the same template and the same data but for different reasons. In task templates, the significance parameter typically appears at the top of the window, near the Task Type and Task Template dropdown menus. Select DoNotTrack if you do not need to track an export.
This parameter applies only to export and aggregation tasks.
-
Reschedule Properties. Allows you to set up a recurring schedule, or to reschedule a failed task to run on a define interval for a certain number of days until it succeeds.
-
Recurring Offset. The Reschedule Recurring Tasks checkbox sets the ApplyOccurrenceOffset task parameter. Valid values are true and false. When true, if the task is running on a recurring schedule, then an offset is applied.
Select Days, Hours, or Minutes and enter a value in the offset interval box to define the OffSetType parameter. The interval value you enter and the offset type you select are stored in the OffSetInterval parameter. The OffSetInterval parameter is the number of days IEE must subtract from "today" when a reading arrives without an associated scheduled read date.
DefaultReadingXmlExport or Custom Report must be selected in System Operations > System Operations > Task Manager > Task Templates >Task Type > Task Template for this parameter to appear.
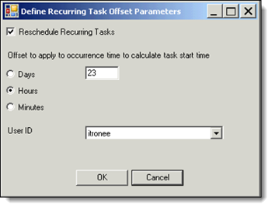
To accommodate Daylight Saving Time (DST) in the spring, open the Define Recurring Task Offset Parameters dialog (Task Template Parameters > Recurring Offset), select Hours, and enter 23 (for a 24-hour task template) or 11 (for a 12-hour task template). Click OK to close the dialog, make sure that the parameter option Perform and Retrieve Self Read is checked, and click Save.
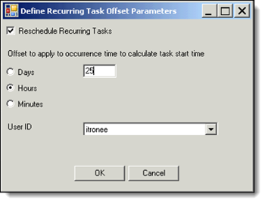
To accommodate Daylight Saving Time (DST) in the fall, open the Define Recurring Task Offset Parameters dialog (Task Template Parameters > Recurring Offset), select Hours, and enter 25 (for a 24-hour task template) or 13 (for a 12-hour task template). Click OK to close the dialog, make sure that the parameter option Perform and Retrieve Self Read is not checked, and click Save.
-
Disable Data Check. Determines whether IEE performs validation, editing, and estimation (VEE) on data required by a task. If the value is True, the cycle ignores the data check and automatically schedules the task, regardless of data availability. Select False to run VEE on the data.
-
Register Read Cycle (Days). Defines a search window for read cycle events. When a data driven read cycle occurs, IEE looks-back this number of days for register data.
This parameter is related to the use of data driven schedules and only applies when the following data cutoff parameters are selected: Run tasks on data up to the time of occurrence, or Run tasks on data up to the selected time.
-
Schedule an Execution Window (Minutes). Defines the number of minutes to allow the following actions:
-
Allow the Cycle Scheduler to schedule a task using the schedule occurrence time as the frame of reference.
-
Allow the task system to execute a task using the task’s requested start time as the frame of reference.
-